NaturoMedica is pleased to announce CardioVIP testing
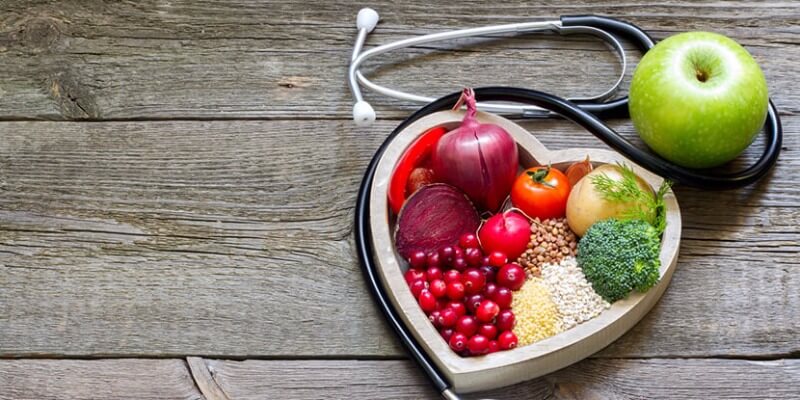

NaturoMedica is excited about the prospect of offering a comprehensive yet cost- effective test called CardioVIP. By using cutting edge testing such as the CardioVIP, our NaturoMedica physicians can provide comprehensive diagnostic evaluation and treatment tailored to an individual's cardiovascular health. Our CardioVIP test offering includes proprietary analyses including advanced cardiovascular risk markers, genetic tests, and micronutrient analysis to determine risk characteristics with more accuracy. Please read through information below to determine if the CardioVIP test is right for you or a family member:
Who should have the CardioVIP test?
- Any individual with known cardiovascular disease
- Any individual with diabetes or pre-diabetes
- Any individual with one of the below risk factors:
- Hypertension
- Abnormal cholesterol levels
- Personal family history of cardiovascular disease
- Age: men >45 years and women >55 years
- Elevated inflammatory biomarkers
- Obesity or being overweight
- Smoking
- Sleep apnea or snoring
- Nutritional deficiencies
What is the CardioVIP test?
Our CardioVIP test is superior to most cardiovascular test offerings and is designed to cover the 5 major components that may contribute to or cause cardiovascular disease. In addition, it offers 2 important genetic tests which may be added risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
1. VASCULAR INFLAMMATION:
- Bio-Monitors –
- Myeloperoxidase (MPO): is a short term predictor of short term risk for cardiovascular event
- Lipoprotein Associated Phoshoplipase A2 (Lp-PLA2): is a strong predictor for a short term risk for a heart attack or stroke
- Highly Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein (hs-CRP): is a well- documented clinical marker of general and cardiac inflammation, even in individuals with normal LDL levels
- F2-Isoprostanes/Creatinine Ratio (F2-IsoPs): is a strong predictor for coronary artery disease. These compounds may promote thrombosis or blood clots
- Microalbumin/Creatinine Ratio: individuals with high urinary microalbumin levels are 3 times more likely to develop cardiovascular disease
- Vitamin D: vitamin D deficiency is associated with increased risk for heart disease. Two-thirds of US population has suboptimal levels of Vitamin D
- Oxidized LDL (OxLDL): more accurately predicts the progression of heart disease and plaque formation in the arteries before symptoms occur. Individuals with high levels of Ox-LDL are 4 times more likely to develop metabolic syndrome within the next 5 years. The presence of increased Ox-LDL levels are associated with presence of coronary heart disease, diabetes and heart attacks
- Micronutrient Testing (associated with vascular inflammation) –

2. DYSLIPIDEMIA & LIPID SUBPARTICLES:
- Bio-Monitors –
- Lipid Panel (Total cholesterol, Triglycerides, HDL-C): a well- established group of tests that can identify patients at risk for cardiovascular disease. However, this test measures blood cholesterol and triglycerides, but does not measure the size of the particles
- Direct LDL: used to determine risk for cardiovascular disease and to monitor effectiveness of natural formulations, drug therapies or lifestyle changes
- Apolipoprotein B (ApoB): individuals with an elevated level of ApoB are 3 times more likely to have a heart attack. Individuals with high ApoB, even though they have normal levels of LDL-C, are at higher risk of heart disease
- Apolipoprotein A1 (ApoA1): low levels are an indication of heart disease, insulin resistance and clotting
- Small Dense LDL (sdLDL Subfractionation: individuals with cardiovascular disease and high levels of sdLDL are 3 times more likely to have disease progression
- HDL2b (HDL Subfractionation): an indicator of how well lipids are removed as well as clearance by the liver
- Lipoprotein Particle Number (LDL-P#): more than 30% of the population has cholesterol-depleted LDL, a condition in which an individual's cholesterol may be normal but their lipoprotein particle numbers, and hence their actual risk, could be much higher than expected
- Lipoprotein a (Lp(a)): individuals with elevated Lp(a) levels are twice as likely to experience a cardiovascular event than those without elevated levels. Lp(a) can rise after females go through menopause, as estrogen aids in keeping Lp (a) levels lower
- Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10): is associated with low HDL levels, and potentially, poor cardiovascular disease outcomes. CoQ10 is critical for cellular energy and is a powerful antioxidant. Levels of ColQ10 decline with age, statin therapy, and low intake of specific nutrients
- Micronutrients Associated with Dyslipidemia –

3. PRE-DIABETES/TYPE 2 DIABETES:
- Bio-Monitors –
- HemoglobinA1c (HbA1c): elevated levels of HbA1c indicate poor glucose control and increased risk for vascular damage. Measures the average glucose levels for over 2-3 months by measuring amount of glucose located on the inside of red blood cells
- Cystatin C-blood: is a marker of renal function and risk of heart failure. High levels are consistently a predictive of cardiovascular event or adverse outcome
- Fasting Glucose: ongoing elevated levels are a sign of insulin resistance generally leading to diabetes or cardiovascular disease. The damage from insulin resistance can exist for years before glucose becomes elevated. Elevated glucose may cause microvascular damage to the eyes, nerves or kidneys
- Insulin: individuals with ongoing elevated levels of insulin are at higher risk for cardiovascular disease. Higher levels of insulin may indicate issues with insulin resistance causing some lipids to become elevated which may hamper weight loss efforts by not allowing body to burn calories effectively. Aids in identifying patients who have insulin resistance but may still have normal glucose levels
- Micronutrient Levels Associated With Diabetes –

4. HYPERTENSION:
- Bio-Monitors –
- N-Terminal proBNP (NT-proBNT): individuals with ongoing elevated levels are at significant risk for heart failure
- Homocysteine: indivdiduals with elevated levels are 2 times more likely to develop coronary artery disease. Homocysteine levels may be elevated due to dietary deficiencies such as low B12, folate, B6 vitamins or due to MTHFR genetic mutations
- Micronutrient Levels Associated With Hypertension –

5. METABOLIC CHARACTERIZATION:
- Bio-Monitors –
- Comprehensive Nutritional Panel: deficiencies in vitamins, minerals, amino acids and antioxidants are associated with chronic degenerative disease processes including cardiovascular disease, stroke, diabetes, metabolic syndrome and osteoporosis
- Thromboxane (AspirinWorks): increased levels may lead to increased risk for heart attack and stroke. AspirinWorks measures constituents in urine which aids in measuring effects of aspirin in individuals post ingestion
- Creatine Kinase: measures both acute and chronic injury to heart cells. Creatine kinase blood levels may rise when taking statins or combo medications which can damage muscle cells
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH): individuals with subclinical or clinical hypothyroidism are at higher risk for heart failure or coronary heart disease. Also, individuals with high levels of TSH may lead to difficulty losing weight which may have high cholesterol levels
- Basic Metabolic Panel: this test measures kidney and liver function, blood sugar levels, electrolyte status and response to certain medications. Abnormal levels may indicate heart or kidney disease
- Hepatic Functions: abnormal enzyme levels may indicate liver damage. The liver is responsible for metabolizing the foods we eat and medications. Insulin resistance or weight gain may promote increased storage of triglycerides in the liver tissues and thus may alter liver function
- CBC: may identify infections in the body, anemia or other disease processes.
- Micronutrient Levels Associated With Weight Management –

GENETICS:
- Apolipoprotein E (ApoE): the ApoE gene predisposes individuals to different levels of cardiovascular diseases in response to dietary fat. Particular ApoE genotypes have been associated with other chronic diseases including Alzheimer's disease
- MTHFR: please click here for more information on this genetic test and the implications related to cardiovascular health
What does the CardioVIP cost?
The patient cost for the CardioVIP testing is $249.*
*Cigna insurance CardioVIP fee will be $299. Medicare coverage is excluded from the CardioVIP.
Your insurance will be billed for the CardioVIP associated lab fees and services.
You will receive an Explanation of Benefits (EOB) from your insurance company listing the insurance claim amount of approximately $4,200 for CardioVIP services. This is not a bill.
Regardless of your insurance coverage, you will not be billed for any remaining balance for the CardioVIP testing that your insurance does not cover.
If you are interested in the CardioVIP test for you or a family member, please contact one of our physicians at 425.557.8900.